Conference
In Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), 2025
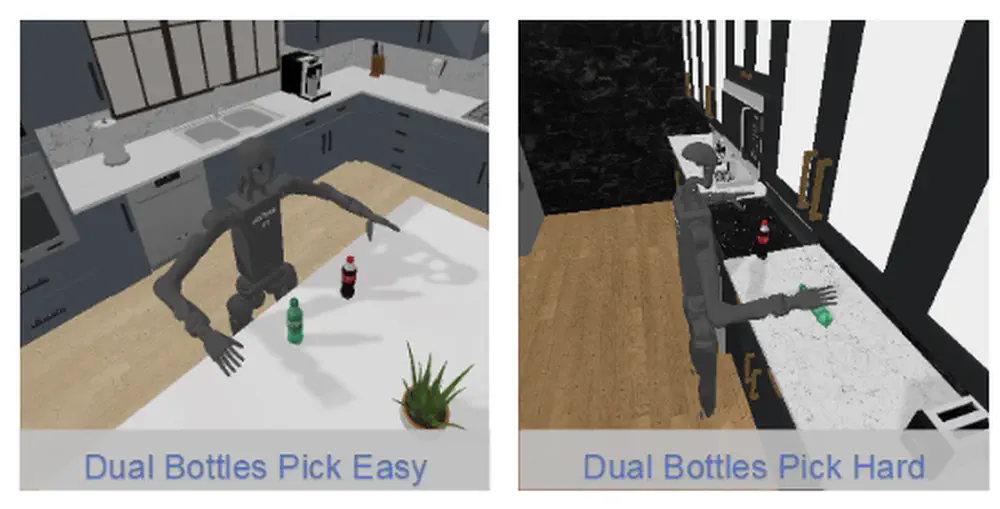
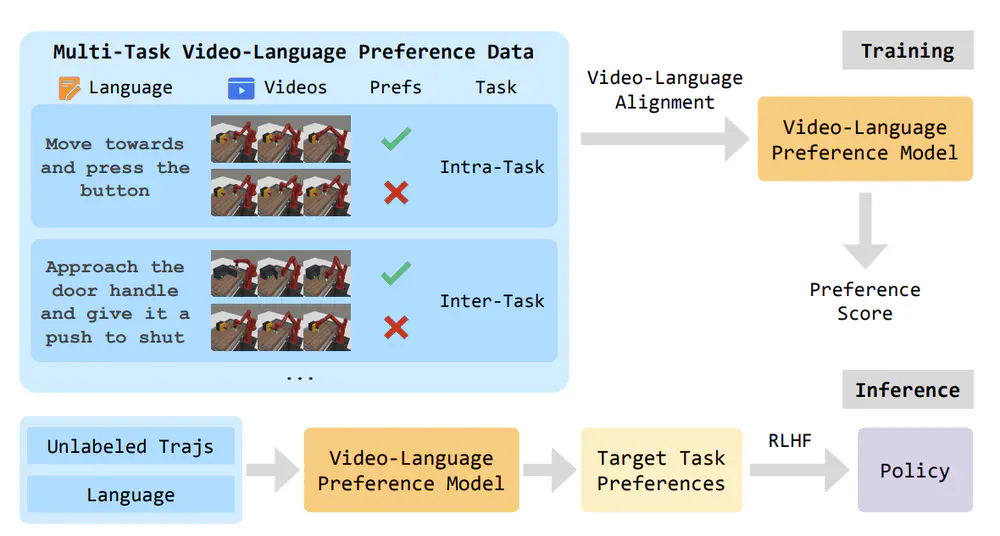
we propose a novel Vision-Language Preference learning framework that learns a vision-language preference model to provide preference feedback for embodied manipulation tasks.
In IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), 2025
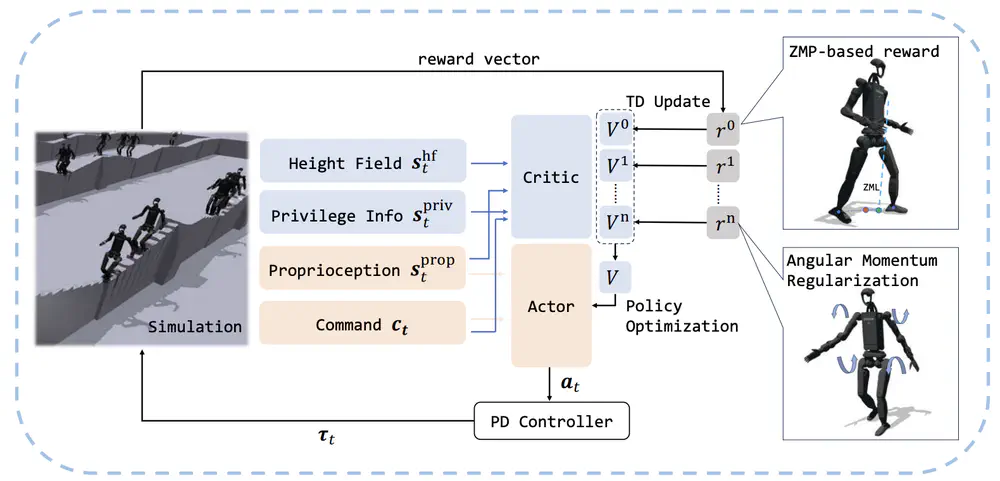
we propose a novel whole-body locomotion algorithm based on dynamic balance and Reinforcement Learning (RL) that enables humanoid robots to traverse extreme terrains, particularly narrow pathways and unexpected obstacles, using only proprioception.
In Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), 2025
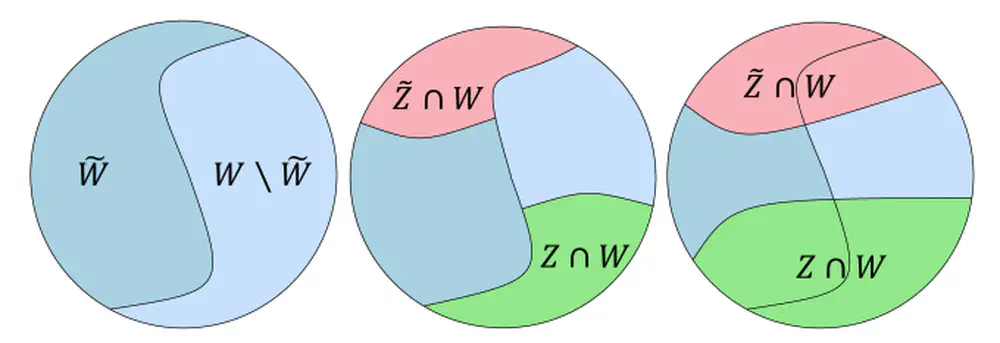
We decompose the reward value in RLHF into two independent components that consists prompt-free reward and prompt-related reward, and propose a new reward learning algorithm by prioritizing data samples based on their prompt-free reward values.
In Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), 2025
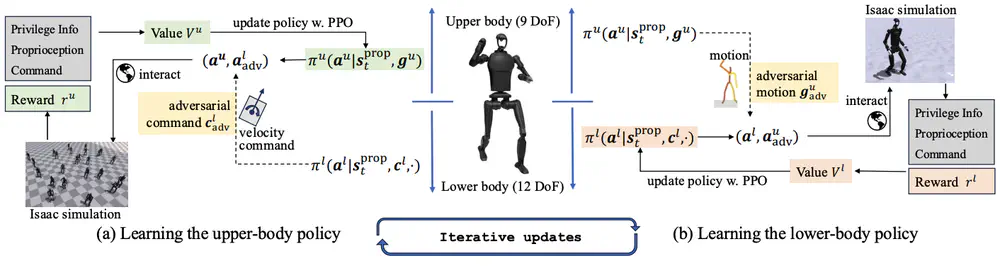
We propose Adversarial Locomotion and Motion Imitation (ALMI) for humanoid robots, which serves as a novel framework for loco-manipulation tasks, enabling adversarial policy learning between upper and lower body.
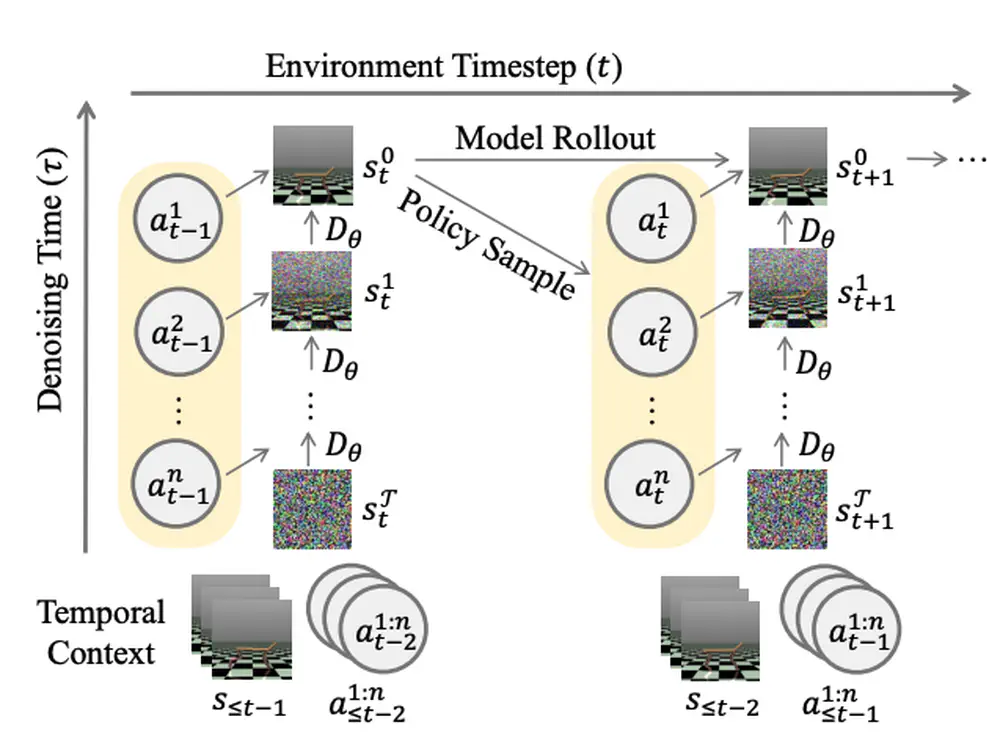
In Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), 2025
We propose Diffusion-Inspired Multi-Agent world model (DIMA), a novel framework for multi-agent reinforcement learning that leverages diffusion models to reduce modeling complexity and improve sample efficiency.
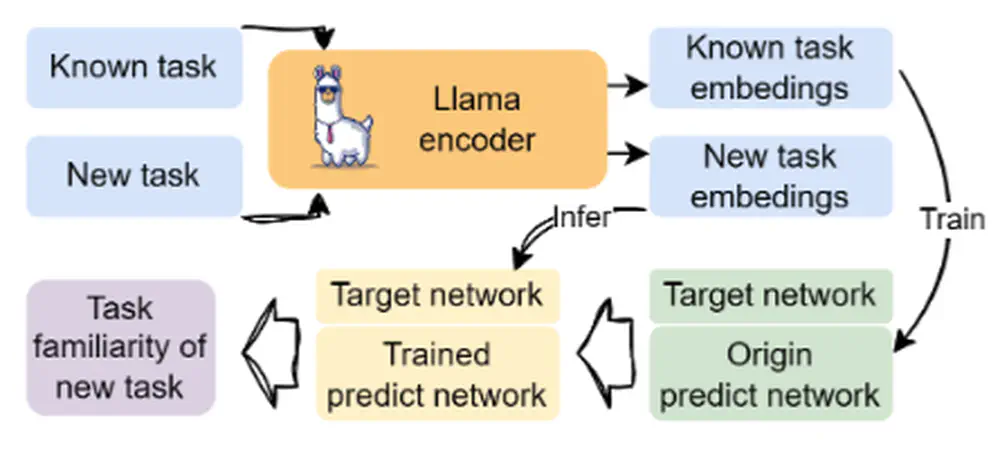
In Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), 2025
We propose CURE, a method that splits LLM planning uncertainty into epistemic and intrinsic parts for more reliable robot decision-making.
In Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), 2025
we propose HumanoidGen, an automated task creation and demonstration collection framework that leverages atomic dexterous operations and LLM reasoning to generate relational constraints.
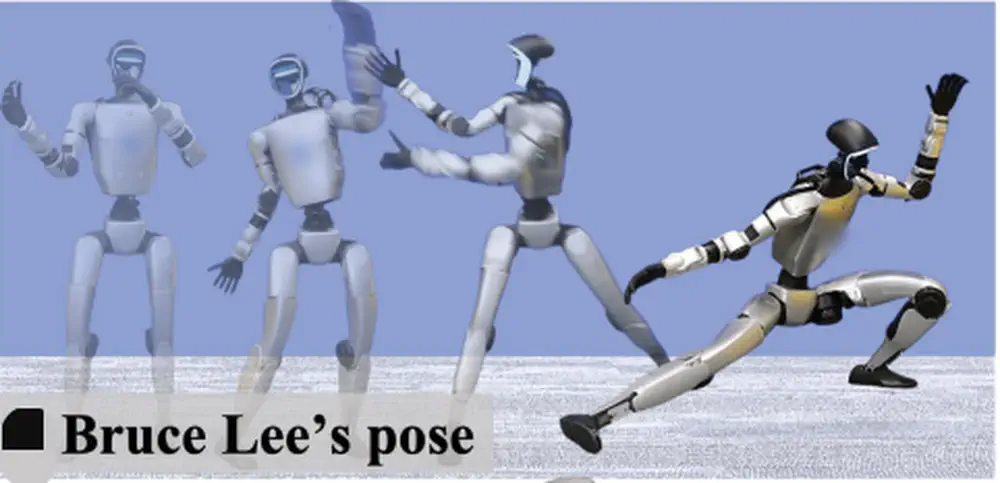
In Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), 2025
We propose a physics-based humanoid control framework, aiming to master highly-dynamic human behaviors such as Kungfu and dancing through multi-steps motion processing and adaptive motion tracking.